In the world of precision, calibration is not just a routine—it is a necessity. Whether you’re working in pharmaceuticals, healthcare, manufacturing, food & beverage, aerospace, or automotive, every measurement matters. One incorrect reading can lead to failed audits, product recalls, or even safety hazards. That’s why choosing the right type of calibration is critical for your business.
In this guide, we’ll explore the various types of calibration, how to determine the right one for your equipment, and how expert calibration services like Prism Calibration can ensure your instruments are performing with absolute accuracy.
What is calibration?
Calibration is the process of comparing the output of a measuring instrument to a known standard and adjusting it to eliminate any deviations. It ensures that the measurements taken by your equipment are accurate, consistent, and traceable to national or international standards.
Why is calibration important?
- To ensure accuracy and reliability
- To maintain compliance with regulatory bodies like ISO, NABL, FDA
- To reduce production errors and product recalls
- To improve customer trust and safety
- To ensure instruments work at peak efficiency
Understanding different types of calibration
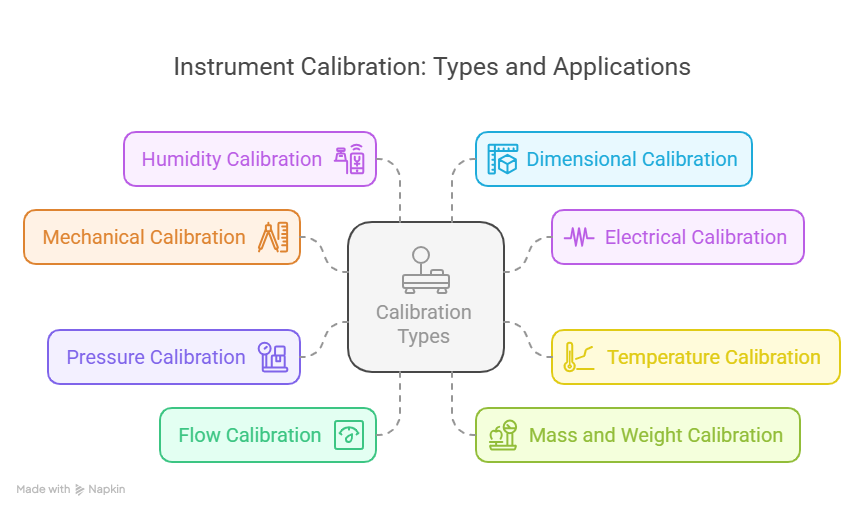
Not all instruments are calibrated the same way. Based on what the device measures, there are different calibration types.
1. Mechanical calibration
Used for: Vernier calipers, micrometers, dial indicators, torque wrenches, and more.
Purpose: Checks dimensional accuracy, linearity, and mechanical movements.
✅ Example: A torque wrench used in assembly lines must apply the correct torque to avoid product damage or failure.
2. Electrical calibration
Used for: Multimeters, oscilloscopes, voltage testers, insulation resistance testers, etc.
Purpose: Verifies voltage, current, resistance, frequency, and signal parameters.
✅ Example: A multimeter in an electronics lab must give precise voltage and resistance readings to avoid incorrect circuit setups.
3. Temperature calibration
Used for: RTDs, thermocouples, infrared thermometers, temperature controllers.
Purpose: Ensures accurate temperature readings in critical applications.
✅ Example: In a pharmaceutical cold storage unit, even a 1°C deviation can damage sensitive vaccines.
4. Pressure calibration
Used for: Pressure gauges, sensors, transmitters, barometers.
Purpose: Maintains accuracy of pressure measurements under varying conditions.
✅ Example: In chemical processing plants, incorrect pressure readings may lead to leakage, system failures, or safety hazards.
5. Flow calibration
Used for: Flow meters, mass flow controllers, rotameters.
Purpose: Ensures correct flow rate measurements of liquids and gases.
✅ Example: In water treatment facilities, flow meters must be calibrated to ensure proper dosage of chemicals.
6. Mass and weight calibration
Used for: Balances, weighing scales, load cells.
Purpose: Confirms weight measurement accuracy with reference standards.
✅ Example: In pharmaceuticals, accurate weighing of active ingredients is critical to drug safety and efficacy.
7. Humidity calibration
Used for: Hygrometers, humidity data loggers, environmental chambers.
Purpose: Validates humidity sensors used in sensitive production environments.
✅ Example: In electronics manufacturing, excessive humidity can lead to corrosion or failure of components.
8. Dimensional calibration
Used for: Gauges, height gauges, measuring tapes, rulers.
Purpose: Verifies dimensions in length, height, or diameter measurements.
Specialized calibration services by prism calibration
At Prism Calibration Centre, we offer advanced and industry-specific calibration solutions, including:
- Gas Detector Calibration
- Sound Level Meter Calibration
- pH and Conductivity Meter Calibration
- Lux Meter Calibration
- UV and IR Meter Calibration
All calibrations are conducted in accordance with ISO/IEC 17025 standards and are traceable to NABL-accredited labs.
How to choose the right calibration type

Selecting the correct type of calibration for your instruments involves multiple factors:
1. Know what your instrument measures
Each measuring instrument is designed for a specific physical parameter: temperature, pressure, flow, electrical signal, etc. Calibration should match this measurement type.
2. Follow manufacturer recommendations
Always refer to the equipment manual for recommended calibration intervals and procedures.
3. Consider industry standards and regulations
Industries like pharmaceuticals, food, healthcare, and aerospace require calibration as per standards like ISO, NABL, FDA, GMP, WHO, and GLP.
4. Assess operational criticality
For high-risk instruments that impact product quality, frequent and high-precision calibration is a must.
5. Evaluate environmental factors
Instruments exposed to heat, dust, humidity, or chemicals may require more frequent calibration.
Conclusion
Choosing the right type of calibration for your instruments isn’t just about compliance—it’s about ensuring precision, safety, and operational excellence. From mechanical and electrical to pressure and temperature calibration, each method plays a unique role in maintaining the accuracy of your equipment.
Whether you’re operating in pharmaceuticals, food processing, manufacturing, or research labs, it’s important to assess your equipment’s usage, environment, and regulatory requirements before deciding on the calibration type.
At Prism Calibration Centre, we bring industry expertise, NABL-accredited processes, and a wide range of calibration solutions under one roof. Let us help you maintain your instruments at the highest standards of accuracy and performance.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
There are several calibration types including mechanical, electrical, temperature, pressure, flow, mass & weight, humidity, and dimensional calibration—each designed for specific instrument categories.
Calibration frequency depends on the equipment type, its usage, industry regulations, and environmental conditions. Most instruments should be calibrated annually, but critical equipment may require quarterly or biannual calibration.
Industries like pharmaceuticals, food, and healthcare require strict measurement accuracy. Calibration ensures compliance with GMP, FDA, ISO, and WHO guidelines, which is essential to avoid penalties, recalls, or safety issues.
Calibration checks and adjusts an instrument to a known standard, while validation ensures that a process consistently produces results meeting pre-defined criteria. Both are important for quality assurance.







