Biomedical equipment, such as patient monitors, infusion pumps, and imaging systems, is vital for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and patient care. However, these devices can drift from their original settings over time, leading to inaccurate readings and potential risks. Biomedical calibration services ensure that your medical equipment operates within specified tolerances, maintaining measurement accuracy and regulatory compliance.
At Prism Calibration, we specialize in providing accredited calibration laboratories and FDA-compliant calibration services to meet the unique needs of healthcare facilities. Our expertise ensures that your equipment adheres to ISO 17025 calibration standards and IEC 60601 equipment standards, guaranteeing the highest levels of safety and reliability.
Why biomedical equipment needs calibration
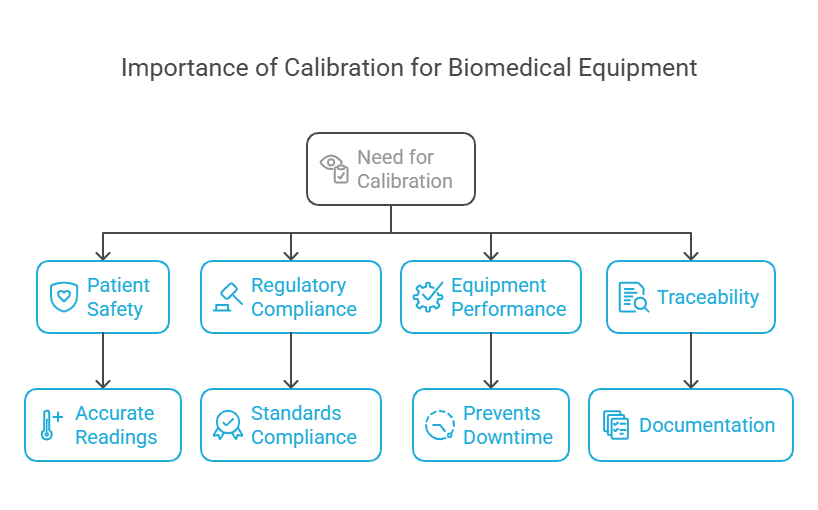
Calibration is not just a regulatory requirement; it’s a cornerstone of patient safety and operational efficiency. Here’s why calibration is essential for biomedical equipment:
- Patient Safety: Accurate readings from medical devices are critical for diagnosis and treatment. Calibration ensures that your equipment provides reliable data, reducing the risk of errors.
- Regulatory Compliance: Healthcare facilities must comply with standards like ISO 17025 and IEC 60601. Regular calibration ensures compliance and avoids penalties.
- Equipment Performance: Calibration maintains the accuracy and reliability of your devices, preventing downtime and costly repairs.
- Traceability: Calibration provides documented proof of compliance through calibration certificates, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Tips for Choosing the Right Biomedical Calibration Provider

Selecting the right calibration provider is crucial for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of your biomedical equipment. Here are some tips to help you make the right choice:
1. Ensure Compliance with ISO 17025 Certification
- Choose a provider that is ISO 17025 certified. This ensures their calibration processes meet global standards and are traceable, providing you with confidence in their measurement accuracy and regulatory compliance.
2. Verify FDA and IEC 60601 Compliance
- Ensure the provider offers FDA-compliant calibration services and adheres to IEC 60601 equipment standards. These certifications are critical for maintaining patient safety and meeting regulatory requirements.
3. Evaluate Their Expertise and Experience
- Look for a provider with extensive experience in biomedical calibration services. A proven track record in the healthcare industry ensures they understand the unique challenges of calibrating medical devices.
4. Check Their Calibration Procedures
- Ensure the provider follows validated calibration procedures and uses advanced testing methods. This guarantees accurate results and minimizes the risk of errors.
5. Prioritize Data Logging and Traceability
- Choose a provider that offers data logging and calibration certificate traceability. This ensures complete documentation and compliance with accreditation and regulatory standards.
6. Assess Their Risk Management Practices
- A reliable provider will have a comprehensive risk management plan to address failure modes and implement preventive measures. This reduces the likelihood of equipment failure and ensures continuous operation.
7. Opt for On-Site Calibration Services
- Select a provider that offers on-site calibration to minimize equipment downtime. This is especially important for healthcare facilities where device availability is critical.
8. Review Their Customer Support
- Choose a provider that offers excellent customer support and guidance throughout the calibration process. This ensures a smooth experience and quick resolution of any issues.
9. Look for Accreditation from Recognized Bodies
- Ensure the provider is accredited by recognized bodies like NABL (National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories). This guarantees their services meet international standards.
10. Consider Their Turnaround Time
- A good provider will offer quick turnaround times without compromising on quality. This minimizes disruptions to your operations and ensures your equipment is back in service promptly.
11. Ask About Preventive Maintenance Plans
- Choose a provider that offers preventive maintenance plans to extend the lifespan of your equipment and reduce the risk of unexpected failures.
12. Verify Their Calibration Documentation
- Ensure the provider provides detailed calibration certificates, calibration reports, and calibration records. This documentation is essential for audits and compliance.
Calibration Process for Biomedical Equipment
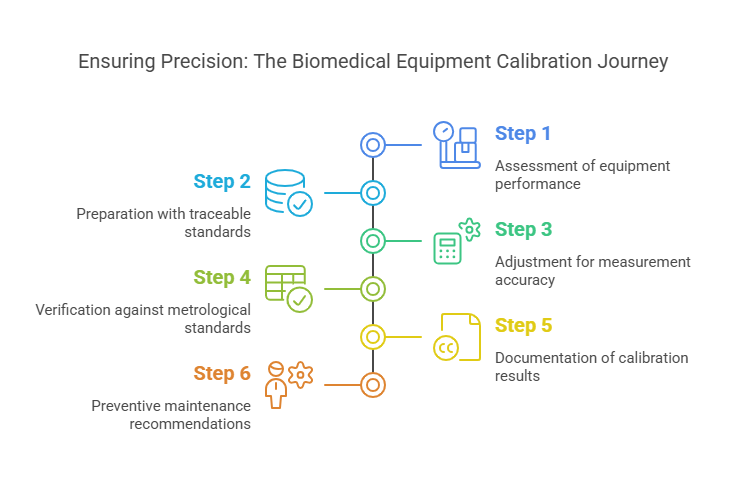
At Prism Calibration, we follow a meticulous step-by-step calibration process to ensure your biomedical equipment meets the highest standards. Here’s how we do it:
Step 1: Assessment
- Evaluate the equipment’s performance and identify calibration needs.
- Determine the appropriate calibration intervals based on usage and regulatory requirements.
Step 2: Preparation
- Use traceable standards and reference instruments for comparison.
- Ensure the calibration environment is controlled to avoid external factors affecting the results.
Step 3: Adjustment
- Fine-tune the equipment to correct any deviations from the standard.
- Use advanced tools and techniques to achieve measurement accuracy.
Step 4: Verification
- Test the equipment to ensure it meets metrological standards.
- Perform multiple tests to confirm consistency and reliability.
Step 5: Documentation
- Provide detailed calibration certificates that include performance data, adjustments made, and compliance information.
- Ensure the documentation is ready for audits and inspections.
Step 6: Preventive Maintenance
- Recommend calibration intervals and maintenance tips to avoid future errors.
- Offer on-site calibration services for added convenience.
Importance of Global Standards in Biomedical Calibration
Adhering to global standards is essential for ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and compliance of your biomedical equipment. Here are the key standards we follow:
ISO 17025 Certification
- Ensures the competence of testing and calibration laboratories.
- Guarantees measurement accuracy and traceability.
IEC 60601 Equipment Standards
- Specifies safety and performance requirements for medical electrical equipment.
- Ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
FDA Compliance
- Meets the requirements of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for medical devices.
- Ensures patient safety and operational efficiency.
FAQs About Biomedical Equipment Calibration
Biomedical equipment calibration is the process of adjusting and verifying the accuracy of medical devices to ensure they meet metrological standards.
Calibration ensures patient safety, regulatory compliance, and equipment performance.
The calibration interval depends on usage and regulatory requirements, typically ranging from 6 to 12 months.
ISO 17025 certification ensures the competence of testing and calibration laboratories, guaranteeing measurement accuracy and traceability.
Yes, we offer on-site calibration services to minimize equipment downtime and ensure convenience.
We serve healthcare facilities, hospitals, diagnostic centers, and medical device manufacturers.
Yes, we provide detailed calibration certificates for audits and compliance.
Conclusion
Choosing the right biomedical equipment calibration provider is crucial for ensuring patient safety, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency. At Prism Calibration, we offer accredited calibration laboratories, FDA-compliant calibration services, and on-site calibration to meet the unique needs of healthcare facilities. Our adherence to ISO 17025 calibration standards and IEC 60601 equipment standards ensures the highest levels of accuracy and reliability.
Contact us today to learn more about our biomedical calibration services and how we can help you maintain the performance and compliance of your medical devices.
Author Bio
Mr. Parthiv Kinariwala is a leading expert in calibration and testing services, with over 20 years of experience in the industry. As the founder of Prism Calibration, established in 2004, Mr. Kinariwala has been at the forefront of delivering precise and reliable calibration, testing, and validation solutions across various industries. His expertise in providing services that meet international calibration standards has earned the trust of major clients, including Reliance Industries, Zydus Cadila, Indian Oil, ONGC, Adani, and Tata.
With a deep understanding of instrumentation, measurement accuracy, and industrial testing, Mr. Kinariwala ensures that each client receives exceptional service tailored to their specific needs. His unwavering commitment to quality and precision has established Prism Calibration as a trusted partner for some of the largest and most respected organizations in the industry.