At Prism Calibration, we are your trusted partner for NABL-accredited calibration services and ISO 17025-certified solutions for laboratory instruments. Whether you operate in the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, agrochemical, or research industry, our expert team ensures your lab equipment delivers precise, reliable, and consistent measurements. In this guide, we’ll explore the importance of calibration, its benefits, and how our tailored services can help you achieve regulatory compliance, measurement accuracy, and operational excellence.
Laboratory equipment calibration is the process of adjusting and verifying the accuracy of instruments to ensure they meet metrological standards. Calibration involves comparing an instrument’s readings against traceable standards or reference instruments to detect and correct any deviations. This process is critical for maintaining the integrity of experimental data, ensuring regulatory compliance, and achieving measurement accuracy.
At Prism Calibration, we specialize in scientific instrument calibration, analytical instrument calibration, and precision measurement services. Our team of experts uses state-of-the-art equipment and follows industry best practices to deliver calibration services that meet the unique needs of your industry.
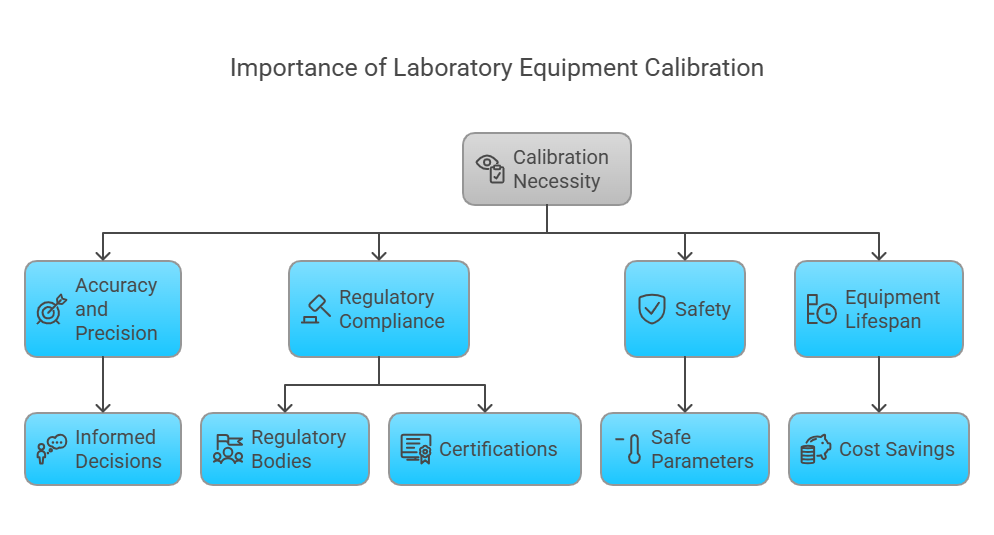
Calibration is not just a regulatory requirement; it’s a fundamental aspect of maintaining reliable and efficient laboratory operations. Here’s why calibration is essential:
Calibration ensures that your instruments provide measurements aligned with traceable standards, allowing you to make informed decisions based on accurate data.
Without proper calibration, instruments like UV cabinets, hot air ovens, and pH meters can produce skewed results, leading to costly errors.
Regulatory bodies such as the FDA, ISO, and ASTM require regular calibration of lab instruments to maintain compliance.
Certifications like ISO 17025 and NABL accreditation are often mandatory for laboratories, and calibration is a key component of these certifications.
In many laboratories, precise measurements are crucial to safety. For example, inaccurate temperature readings in a hot air oven or muffle furnace could lead to dangerous outcomes.
Calibration ensures that your instruments operate within safe parameters, reducing the risk of accidents.
Regular calibration and preventive maintenance help extend the lifespan of your lab instruments, saving you money in the long run.
By identifying and addressing issues early, calibration prevents costly breakdowns and downtime.
Regular calibration offers numerous advantages for laboratories, including:
Ensures your data is reliable and consistent, which is critical for research, quality control, and compliance.
Helps you meet industry standards and avoid penalties or legal issues.
Provides documented proof of compliance through calibration certificates.
Prevents costly operational errors and equipment failures by identifying issues early.
Reduces the need for expensive repairs or replacements.
Minimizes downtime by ensuring your instruments are always in optimal condition.
Improves workflow efficiency by reducing the likelihood of errors.
Provides documented proof of compliance for audits and inspections.
Ensures transparency and accountability in your calibration processes.

At Prism Calibration, we follow a meticulous step-by-step calibration process to ensure your instruments meet the highest standards. Here’s how we do it:
Evaluate the instrument’s performance and identify calibration needs.
Determine the appropriate calibration intervals based on the instrument’s usage and industry requirements.
Use traceable standards and reference instruments for comparison.
Ensure the calibration environment is controlled to avoid external factors affecting the results.
Fine-tune the instrument to correct any deviations from the standard.
Use advanced tools and techniques to achieve measurement accuracy.
Provide detailed calibration certificates that include the instrument’s performance data, adjustments made, and compliance information.
Ensure the documentation is ready for audits and inspections.
Recommend calibration intervals and maintenance tips to avoid future errors.
Offer on-site calibration services for added convenience.

We adhere to the highest industry standards and certifications to ensure the quality and reliability of our calibration services. These include:
Ensures testing and calibration competence.
Demonstrates our commitment to measurement accuracy and regulatory compliance.
Guarantees the accuracy and reliability of our services.
Provides assurance that our calibration processes meet metrological standards.
Meets requirements for industries like pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and research.
Ensures your instruments are compliant with FDA, ISO, and ASTM regulations.
Even the best instruments can face calibration issues. Here are some common errors and how to avoid them:
Issue: Mishandling instruments during calibration can lead to inaccurate results.
Solution: Train staff on proper handling techniques and use protective equipment.
Issue: Temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors can affect calibration.
Solution: Perform calibration in a controlled environment and monitor conditions closely.
Issue: Infrequent calibration can lead to undetected deviations.
Solution: Follow recommended calibration intervals based on instrument usage and industry standards.
Issue: Missing or incomplete calibration certificates can lead to compliance issues.
Solution: Maintain detailed records of all calibration activities and ensure they are readily available for audits.
At Prism Calibration, we stand out for our:
Expertise: Years of experience serving industries like pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and research.
Accreditation: NABL-accredited calibration services and ISO 17025 certification.
Comprehensive services: From scientific instrument calibration to equipment validation services, we cover all your needs.
Customer-centric approach: Tailored solutions to meet your specific requirements.
On-site calibration: Convenient services to minimize downtime.
Calibration frequency depends on several factors, including the type of instrument, its usage, and the environment in which it operates. Some instruments may need calibration monthly, while others can be calibrated annually. High-precision or heavily used instruments often require more frequent calibration to maintain accuracy.
While basic calibration tasks can sometimes be performed in-house, most laboratories opt to outsource calibration for critical instruments or when specialized expertise is required. Professional calibration services ensure traceability, accuracy, and compliance with industry standards.
Failure to calibrate instruments regularly can lead to inaccurate readings, compromised data, and potentially costly mistakes. This can result in regulatory non-compliance, compromised product quality, or even safety hazards in certain laboratory settings.
Yes, calibration certificates are essential as they provide documentation that the instrument has been calibrated against recognized standards. These certificates are often required for regulatory compliance, quality assurance, and for maintaining accreditation in industries like pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, and research.
If you notice inconsistent or erratic results, it’s a sign that your instruments may need calibration. Additionally, regular maintenance schedules, industry guidelines, or compliance requirements may specify calibration intervals for your equipment.
To ensure the longevity and performance of your instruments, regularly inspect them for signs of wear and tear, keep them clean, and store them properly in controlled environments. Following the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines can also help preserve accuracy between calibrations.
Several industries, including pharmaceuticals, healthcare, environmental monitoring, food testing, manufacturing, and research, require regular calibration of laboratory instruments to ensure quality, accuracy, and compliance with regulatory standards.
If an instrument fails calibration, it may need adjustments or repairs. The calibration service provider will usually provide a detailed report of the issue and suggest corrective actions, which could involve part replacement, recalibration, or maintenance.
Not all laboratory equipment requires frequent calibration. However, any instrument that is used to measure or analyze data in a scientific or industrial setting should be calibrated periodically to ensure that the results are accurate and reliable.
